- Overview
- Log In For Videos
- Give Feedback
- Seizure Classification
- Unknown Onset Seizure
- Neonatal Seizure
- Epilepsy Classification
- Generalized Epilepsy
- Focal Epilepsy
- Generalized and Focal Epilepsy
- Unknown Epilepsy
- Epilepsy Syndromes
- Epilepsy Etiologies
- Metabolic Etiologies
- Immune Etiologies
- Infectious Etiologies
- Unknown Etiologies
- Encephalopathy
- Epilepsy imitators
TUBEROUS SCLEROSIS
Imaging
Imaging for optimized detection of tuberous sclerosis:
MRI, with thin slice volumetric T1-weighted images, axial and coronal T2-weighted and FLAIR images.
Imaging characteristics of tuberous sclerosis:
- cortical tubers (present in 80% or more patients, cerebellar tubers may also be present)
- subependymal nodules (present in 95% or more patients)
- subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (present in around 10-15% of patients)
- white matter abnormalities and cysts
The pathological and imaging features of cortical tubers can be indistinguishable from those of focal cortical dysplasia (FCD IIb). Hemimegalencephaly has been reported in some patients with tuberous sclerosis.
Imaging in tuberous sclerosis
This is a T2-weighted image of a cortical tuber in an immature brain. There is a localized area of gyral expansion in the right frontal lobe, with abnormal low signal in the underlying white matter. The imaging features of this tuber can be similar to that of a focal cortical dysplasia (FCD type IIb).
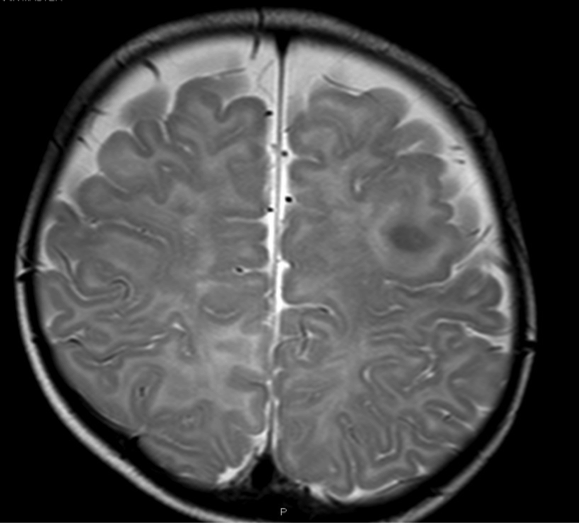
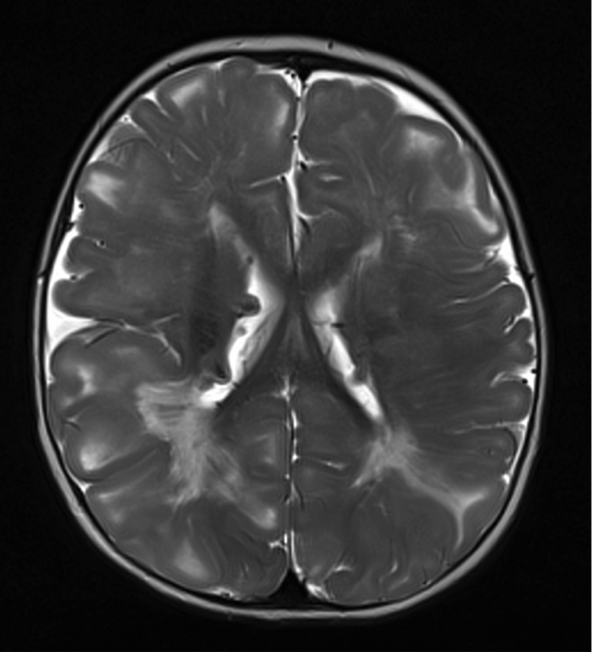
Imaging in tuberous sclerosis
Both images below are from the same patient and show:
- multiple cortical tubers - areas of gyral expansion with thickening of the overlying cortex and abnormal signal in the underlying white matter
- subependymal nodules
- white matter abnormality
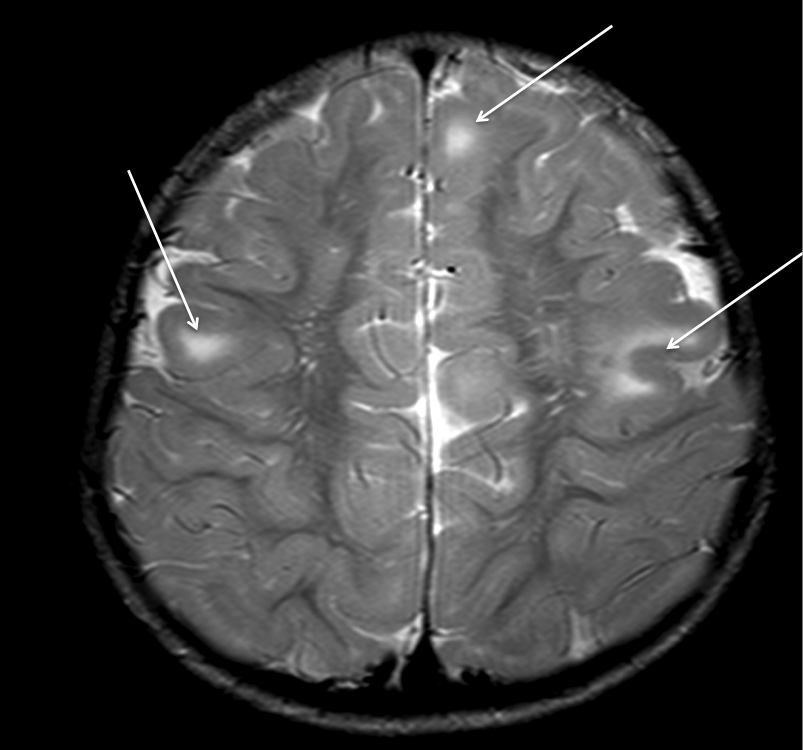
Imaging in tuberous sclerosis
The image below is a T2-weighted image showing cortical tubers in the right and left frontal lobes (arrows).