- Overview
- Log In For Videos
- Give Feedback
- Seizure Classification
- Unknown Onset Seizure
- Neonatal Seizure
- Epilepsy Classification
- Generalized Epilepsy
- Focal Epilepsy
- Generalized and Focal Epilepsy
- Unknown Epilepsy
- Epilepsy Syndromes
- Epilepsy Etiologies
- Metabolic Etiologies
- Immune Etiologies
- Infectious Etiologies
- Unknown Etiologies
- Encephalopathy
- Epilepsy imitators
STROKE
Imaging
Imaging for optimized detection of stroke:
Non contrast CT is helpful for the initial rapid diagnosis of hemorrhagic stroke, and CT angiography can demonstrate causes such as dissection. MRI is the imaging of choice for assessing the detail of ischemic stroke acutely, and the long-term structural sequelae in patients who have post-stroke epilepsy. MRI should include thin slice volumetric T1-weighted images, axial and coronal T2-weighted and FLAIR images. In acute stroke, diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC maps may be required to show areas of ischemia in the first hours after stroke. MRA is also important to assess for stroke etiology (which may include dissection of large vessels, arteriopathy or embolic occlusion). MR imaging with susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) or T2* imaging is helpful for detection of hemorrhage.
Imaging characteristics of acute stroke:
- diffusion restriction, resulting in high signal on DWI and low signal on ADC maps, within minutes from the onset of ischemia
- high signal on T2/FLAIR imaging in the affected area within 6-12 hours
- sulcal effacement and mass effect in the affected area in the first 24-48 hours
- cortical laminar necrosis appearing as a ribbon of high signal on T1 weighted images, after 2 weeks
Imaging characteristics of chronic stroke:
- atrophy, gliosis, porencephaly/encephalomalacia and ex vacuo dilation of the ipsilateral ventricle in the location of the previous acute stroke.
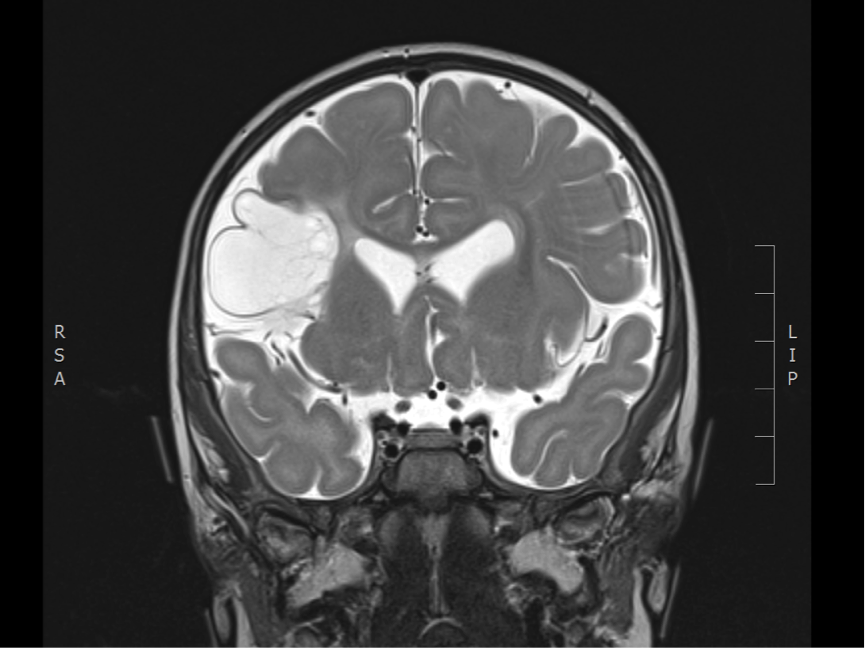
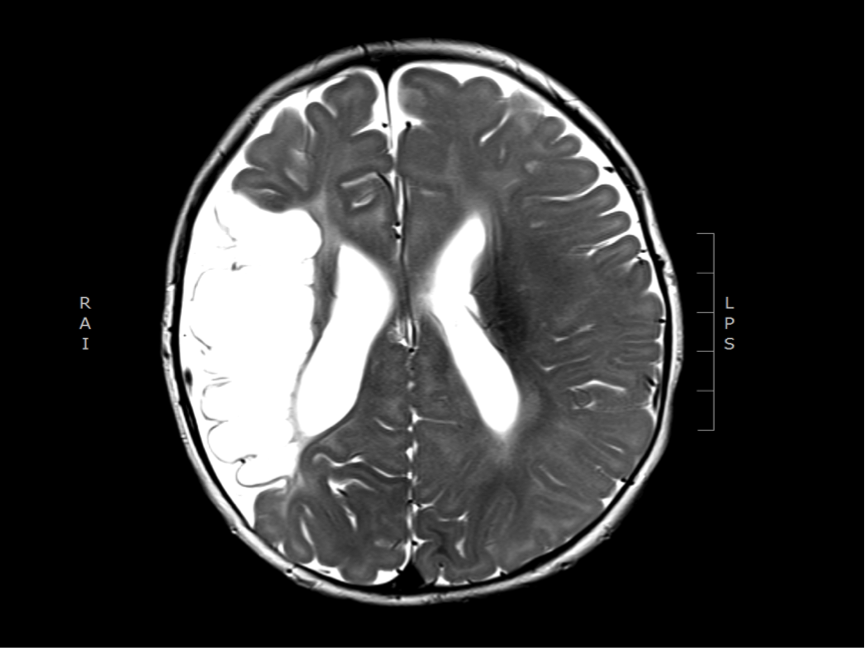
Imaging of chronic stroke
The two images below show the sequelae of a previous middle cerebral artery territory infarction, in a 4 month old infant (congenital stroke), who presented with epileptic spasms. There is a porencephalic cyst in the territory of the right middle cerebral artery with atrophy and gliosis in the cortex at the margins of the cyst.