- Overview
- Log In For Videos
- Give Feedback
- Seizure Classification
- Unknown Onset Seizure
- Neonatal Seizure
- Epilepsy Classification
- Generalized Epilepsy
- Focal Epilepsy
- Generalized and Focal Epilepsy
- Unknown Epilepsy
- Epilepsy Syndromes
- Epilepsy Etiologies
- Metabolic Etiologies
- Immune Etiologies
- Infectious Etiologies
- Unknown Etiologies
- Encephalopathy
- Epilepsy imitators
PORENCEPHALIC CYST
Imaging
Imaging for optimized detection of a porencephalic cyst:
Porencephalic cysts may be seen on cranial USS, CT and MRI. However, MRI is the imaging of choice for assessing the detail of the cyst, the cortex of the cyst margin and for any co-existing structural abnormality related to the antecedent insult. MRI should include thin slice volumetric T1-weighted images, axial and coronal T2-weighted and FLAIR images.
Imaging characteristics of a porencephalic cyst:
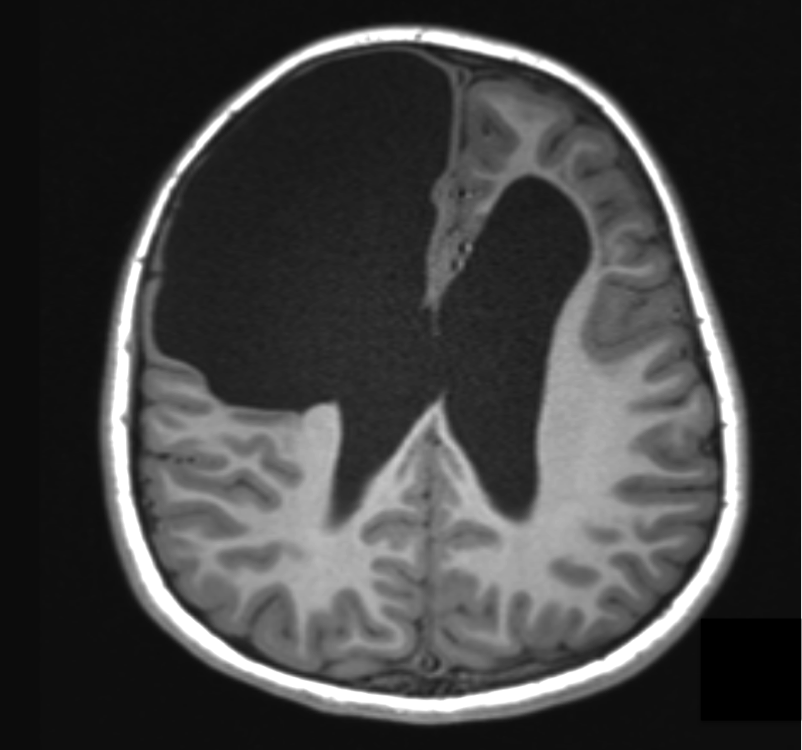
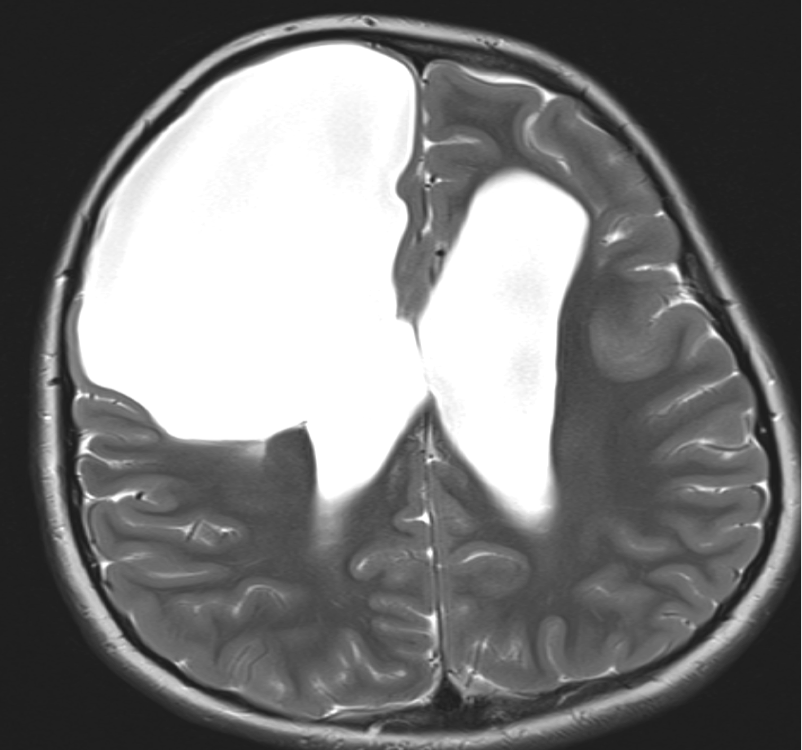
Imaging shows a fluid filled cavity replacing an area of the cerebral hemisphere. There may be cortical atrophy and gliosis around the cyst margin. There may be ex vacuo dilation of the ipsilateral ventricle.
Imaging of a porencephalic cyst
Both images below are from the same patient and illustrate a large porencephalic cyst in the right frontal lobe. The cyst is in communication with the lateral ventricle and has a margin of atrophic cortex, related to its lateral and mesial margins. There is also atrophy in the left frontal lobe, with ex vacuo dilation of the anterior horn of the left ventricle. The porencephalic cyst in this patient is the sequelae of neonatal meningitis, which was complicated by a right frontal abscess.