

- Overview
- Log In For Videos
- Give Feedback
- Seizure Classification
- Unknown Onset Seizure
- Neonatal Seizure
- Epilepsy Classification
- Generalized Epilepsy
- Focal Epilepsy
- Generalized and Focal Epilepsy
- Unknown Epilepsy
- Epilepsy Syndromes
- Epilepsy Etiologies
- Metabolic Etiologies
- Immune Etiologies
- Infectious Etiologies
- Unknown Etiologies
- Encephalopathy
- Epilepsy imitators
LISSENCEPHALY
Imaging
Imaging for optimized detection of lissencephaly:
Whilst lissencephaly may be seen on USS (antenatal and postnatal) and CT, MRI is the imaging of choice for assessing the detail and associated structural abnormalities. MRI should include thin slice volumetric T1-weighted images, axial and coronal T2-weighted and FLAIR images.
Imaging characteristics of lissencephaly type 1:
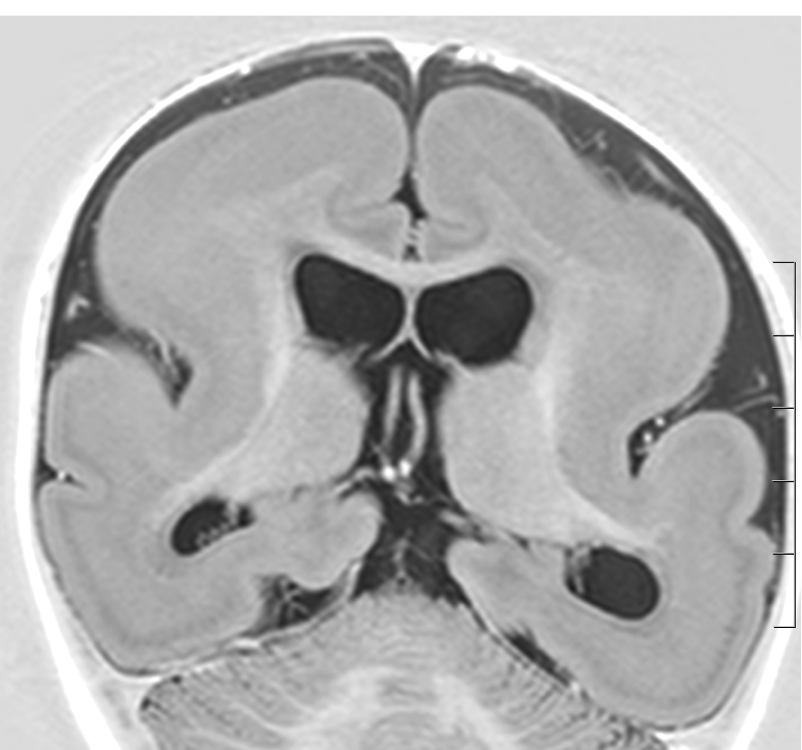
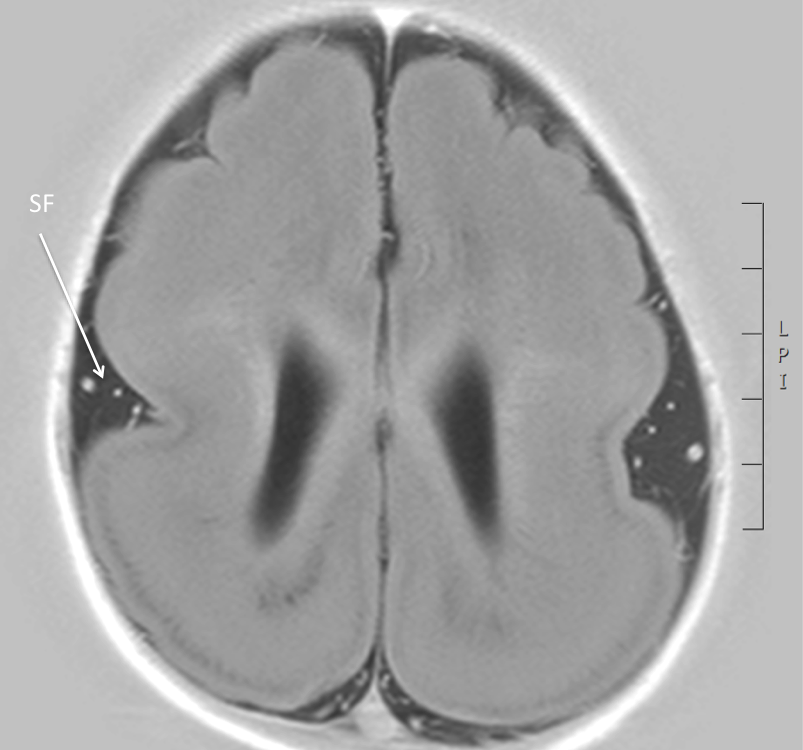
- reduced gyration (resulting in a shallow Sylvian fissure giving a 'figure of 8' appearance)
- cerebral cortical thickening, 12-20mm (instead of 3-4mm)
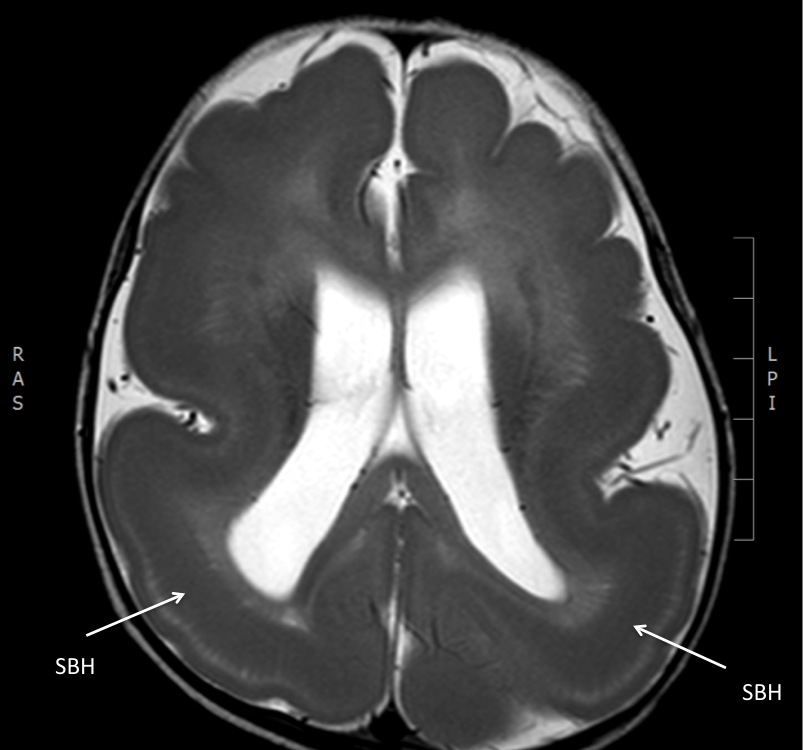
- subcortical band heterotopia is sometimes seen (anterior predominance in DCX pathogenic variants, posterior predominance in LIS1 pathogenic variants)
- other structural brain abnormalities may be seen such as enlarged ventricles and hypoplastic corpus callosum
Imaging in lissencephaly type 1
The images below are all from the same patient. They show reduced gyration, a shallow Sylvian fissure (SF, arrow), thickening of the cortex and subcortical band heterotopia, appreciated over posterior regions (SBH, arrows).
Imaging characteristics of lissencephaly type 2 can include:
- lack of normal sulcation (resulting in a shallow Sylvian fissure giving a 'figure of 8' appearance)
- nodular cortical surface
- associated abnormalities, related to associated syndromes